3D printing applications – in what industries and how are 3D printers used?
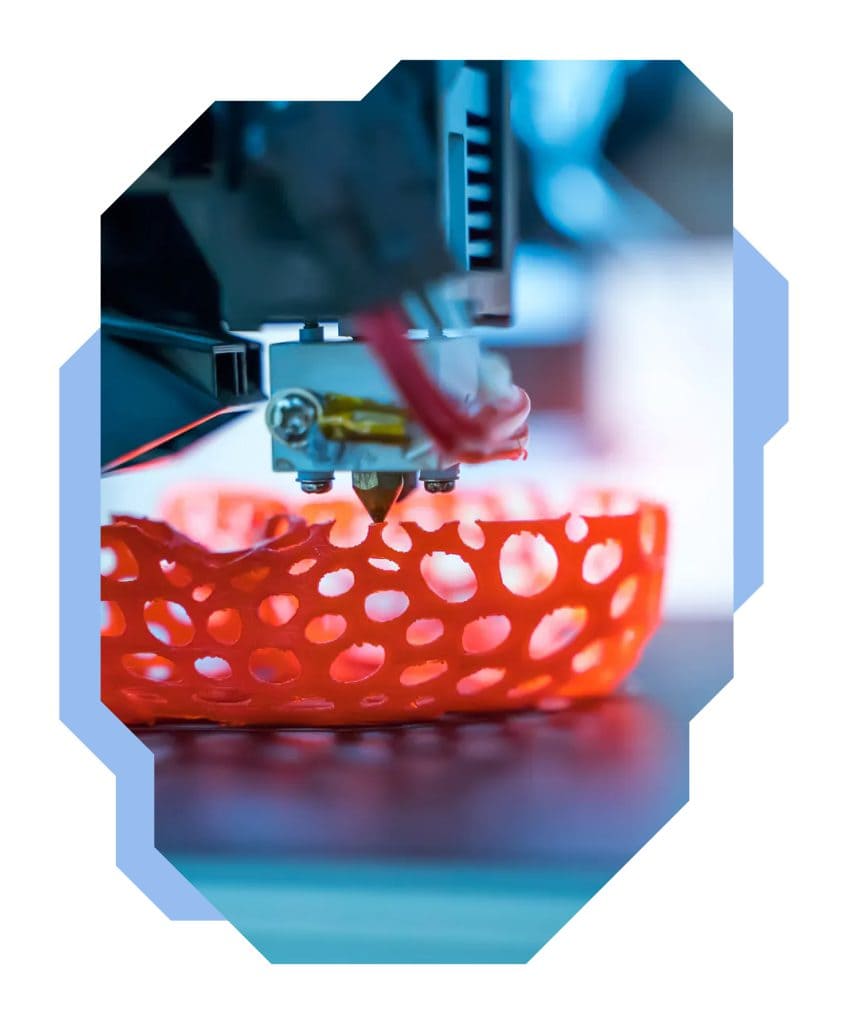
3D printing is a technique for producing physical, three-dimensional objects previously designed using 3D modelling software. 3D printing technology is now widely applicable owing to a variety of materials and 3D printers. In addition to the educational benefits that simple printers offer to primary and secondary schools, there are more advanced 3D printers that allow this technique to be applied, for example, in prototyping, industry, medicine, construction and in many, many other fields.
3D printer – application
We want to show you where your students can come across 3D printing in the future, and by gaining first-hand experience with this innovative technology already at primary school level, they will gain understanding and familiarity with it.
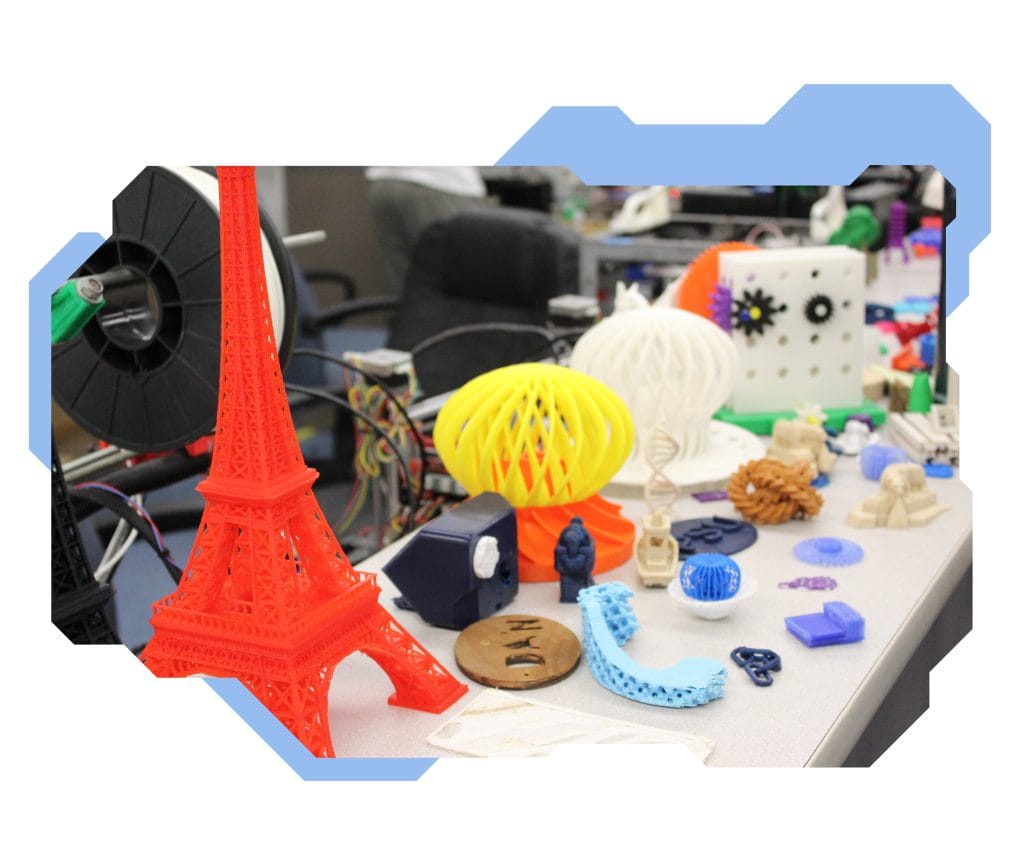


The applications of 3D printing in education
In our previous posts you can read how 3D printing can be applied in education. As a reminder, the device will be used not only to raise competence in 3D printing technology and spatial modelling. What can be printed with a 3D printer? Just about everything! Teaching aids: a plant cell, structures, effigies of famous writers, figurines representing traditional costumes or historical tools, planets, geometric solids, the brain, the heart, and many, many more. The options are unlimited. In addition to this, 3D printing provides invaluable support in the education of children with special educational needs. Physical objects on which every detail is clearly visible allows them to better understand the world around them. Three-dimensional printouts also include all kinds of gadgets, gifts, medals, and trophies that you and your students will create for any occasion.
3D printing application in medicine and dentistry
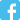
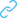
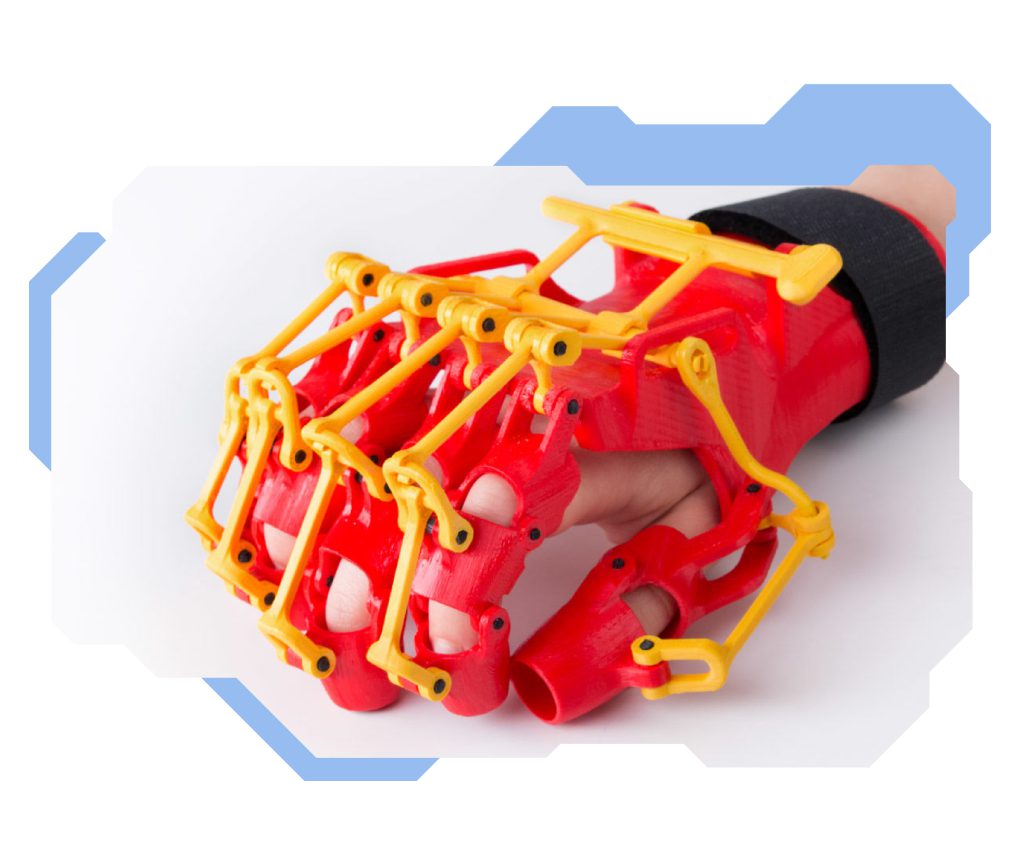
3D printing in medicine? You may not be surprised, but doctors often use specialist models of human organs to study. In addition, printouts of organs from specific patients that can be created with ultrasound and X-ray scans help them prepare for complex procedures. With these 3D printouts, they can perfectly visualise the exact part of a patient’s body that they will be performing surgery on with coloured innervation or tissue structure. This also allows them to perform surgery more efficiently and quickly. After all, practice makes perfect! 3D printing is commonly used to create implants and surgical instruments. Dental implantology also greatly benefits from the accuracy of a 3D printer. Another professional who can benefit from 3D printing technology is a dental technician. The 3D printer allows creating prototypes and models of dental curves or aligners.
3D printing application in construction and architecture
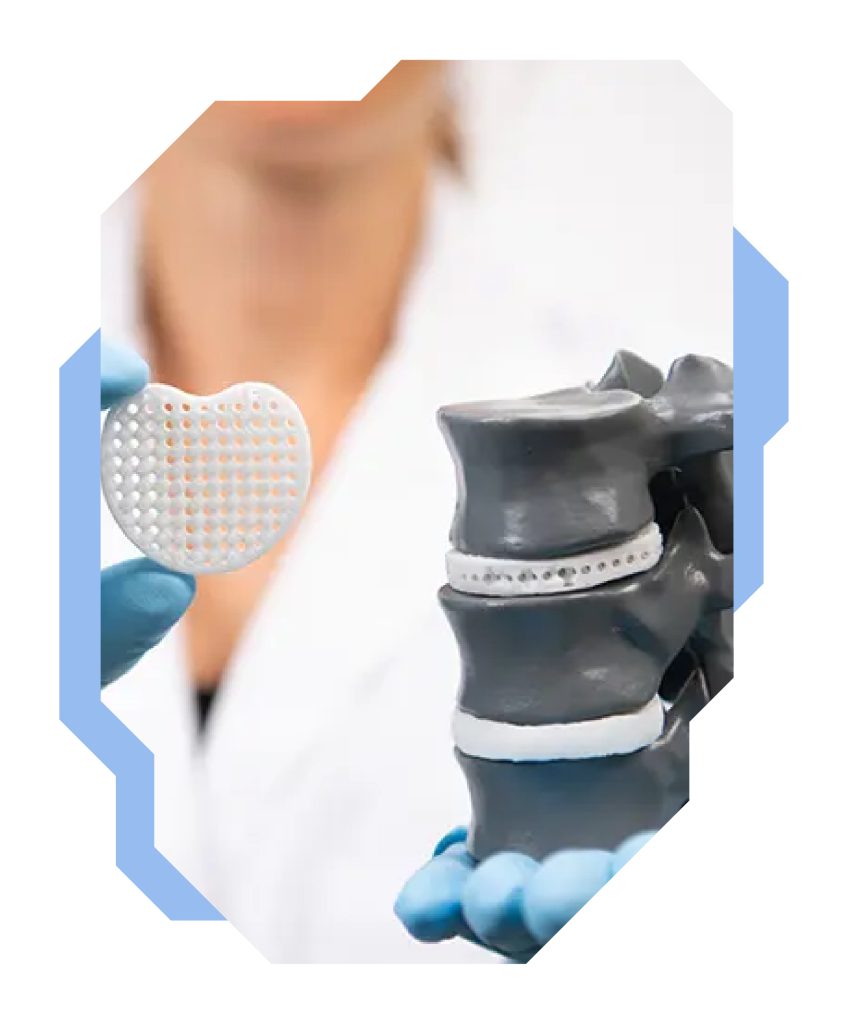
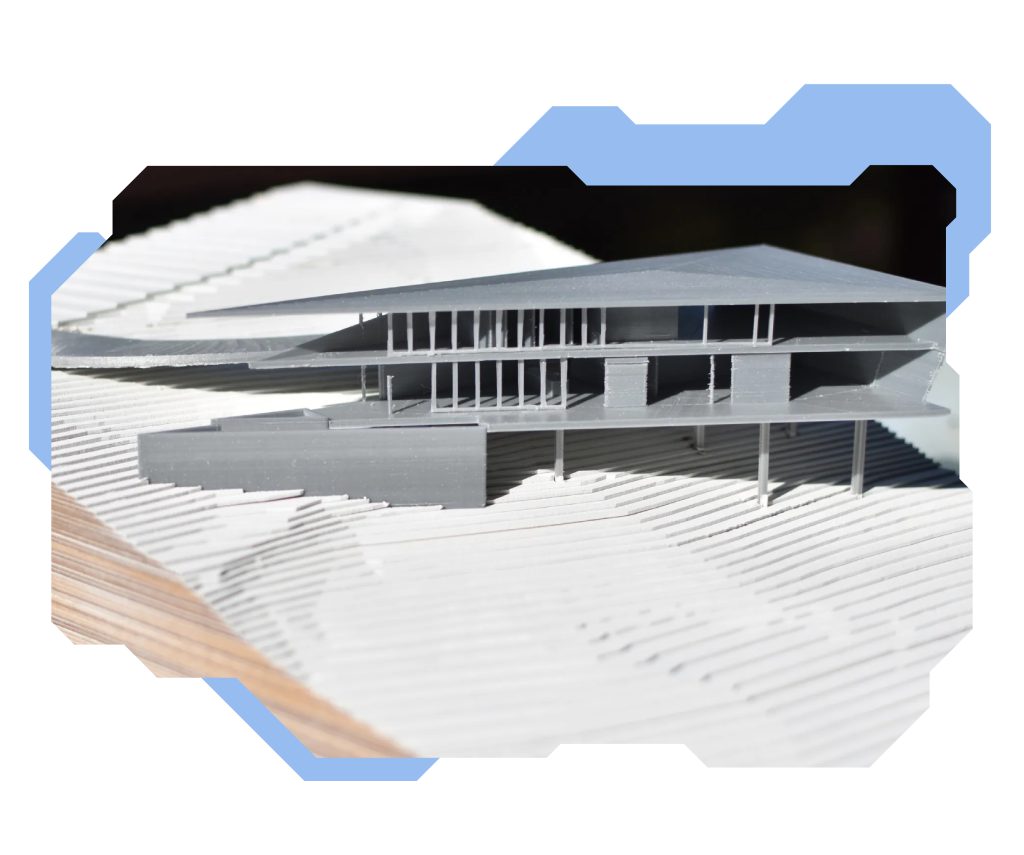
3D printing in architecture is mostly used at the stage of structure design prototyping and mock-ups. Mock-ups have been a well-known practice for many, many years, allowing an architectural firm to show and approve a design with a developer. Full-scale mock-ups are also used to check the basic assumptions of a design. With 3D printing, their creation is easier, cheaper (consulting, adding, and subtracting components already at the 3D modelling stage) and more precise, as they can replicate even the smallest details. In addition, human error is eliminated when creating a mock-up. Furthermore, 3D printing can be used directly in construction. There are already known cases where highly specialised 3D printing companies, such as Apis Core, have printed entire houses and even huge buildings.
3D printing applications in industry
The use of 3D printing in industry is similar. It is used by industrial manufacturers to streamline, accelerate and flexibilise their work. 3D printing is used primarily for fast and accurate prototyping of various industrial machine parts. 3D printing also allows manufacturers to produce some parts that are already finished products faster. It is also applied in the production of items with very complex geometries. Printers with a large print area allow printing quickly and even smaller batches of the so-called low-volume products, which would normally be extremely expensive. In addition, a production plant can quickly produce spare parts for its needs, thus avoiding production downtime.
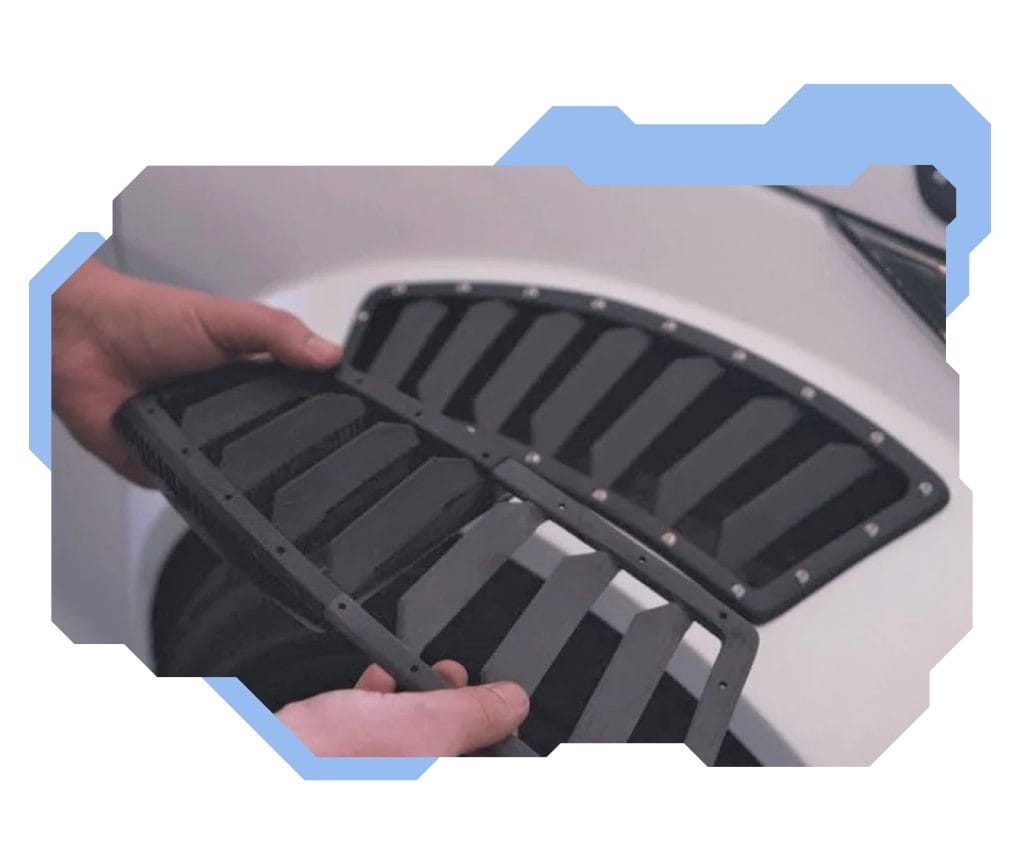

3D printing applications in automotive and aviation industries
3D printing in automotive and aviation industries helps optimise the production process of a vehicle through and through. With its 3D modelling option, it provides support already at the design stage and design verification. As a result, it is often possible to create components with less weight but high quality and strength early on with 3D printers, thus affecting the overall weight of a car or an aeroplane. As in industry, 3D printing technology in automotive and aviation industries is also used to produce spare parts.
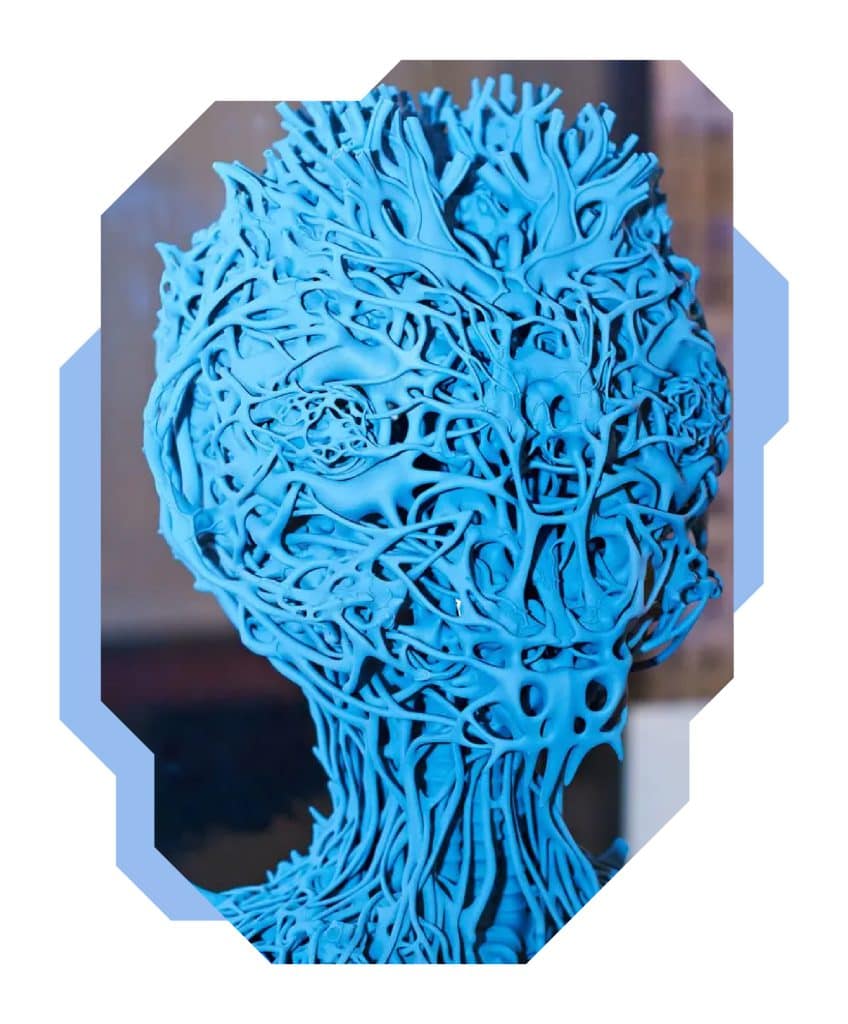
3D printing applications in art
If you are still wondering why the letter A (Arts) was added to the STEM disciplines to form the STEAM methodology, we are here to explain. 3D printing can also be used in art and painting! Design professionals and designers are particularly keen to use it. Sculpture also naturally comes to mind, where 3D printers are finding their followers owing, among other things, to the use of wood-like materials in printing. What about painting? You will be surprised! 3D printing allows us to create the most accurate image reproductions to date, maintaining the highest precision in colour and shadow recreations. Of course, the works created do not have to be reproductions, but also the original paintings.
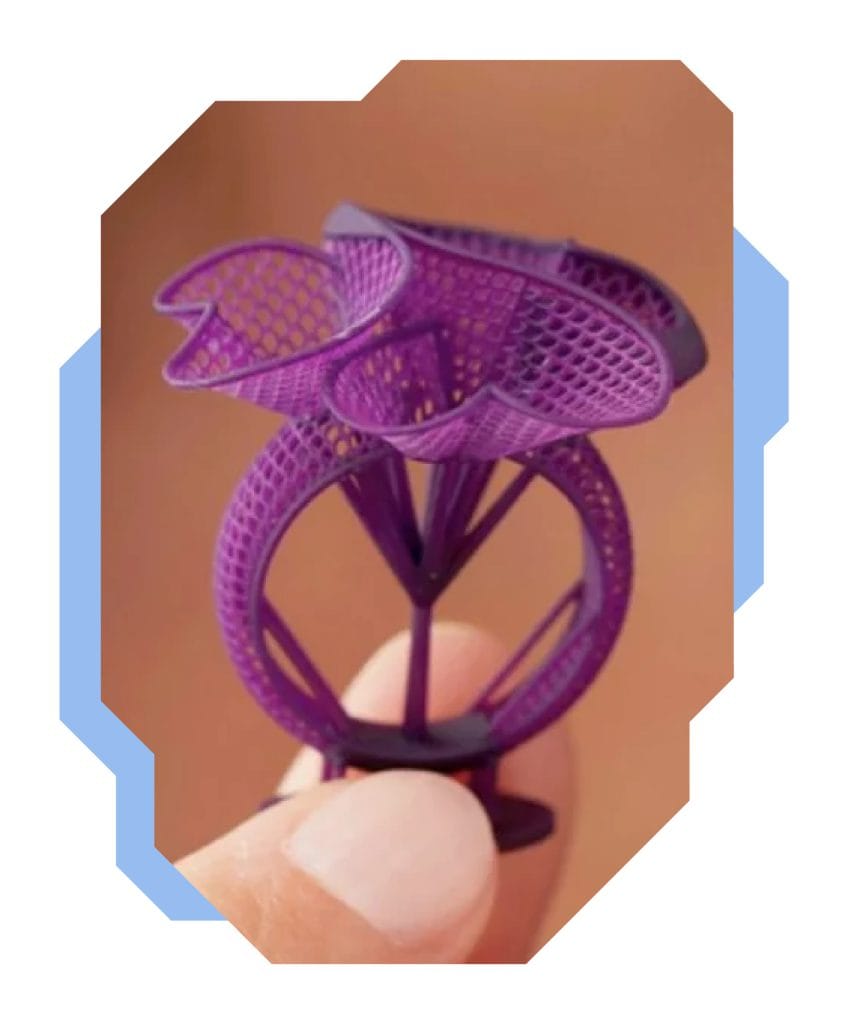


3D printing applications in jewellery
Jewellers also use 3D printing! With it, they create conceptual models or, like architects, show and consult jewellery designs with their clients. In jewellery, 3D models serve as durable and highly accurate casting moulds. This is made possible by the lost-wax casting process.
Why do 3D printers find their way into so many industries?
As you can see 3D printing has several advantages that allow it to be used in so many industries. With the support of highly specialised printers, professionals can produce certain items faster and do not need a vast production scale to make it profitable. 3D printing also enables precision prototyping, and many manufactured parts feature an incredible object weight/strength ratio. The variety of materials that can be 3D printed makes the applications for this technology truly endless.
If you want to book the Skriware demo lesson for your school do not hesitate to contact us at [email protected]!